how do we see color wavelength
For example red light has a longer wavelength than blue light. We can see Yellow by catching the wavelength that directly corresponds to the color or by catching both Red and Green at the same time.
Why Nasa Scientists Observe The Sun In Different Wavelengths Nasa
Colors are specific wavelengths of light reflecting off of objects or matter that humans can see.

. Youre probably familiar with the color wheel which arranges visible colors. Converting Wavelengths to RGB color values. The colour we see is a result of which wavelengths are.
When sunlight hits a beach ball we see only the light that bounces. Visible light waves are the. Light is made up of wavelengths of light and each wavelength is a particular colour.
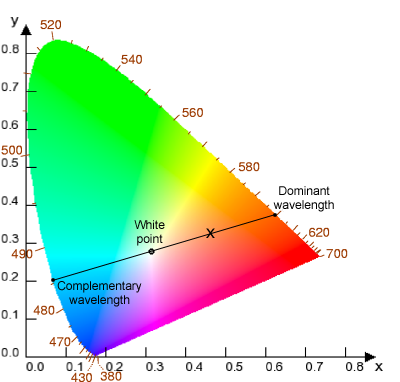
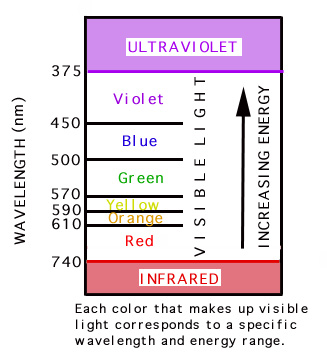
The spectrum ranges from dark red at 700 nm to violet at 400 nm. The colour we see is a result of which wavelengths are reflected back to our eyes. How do we see color wavelength.
The colour we see is a result of which wavelengths are. Sunlight is a mixture of different colors or wavelengths. However the number of waves that passes a certain point in.
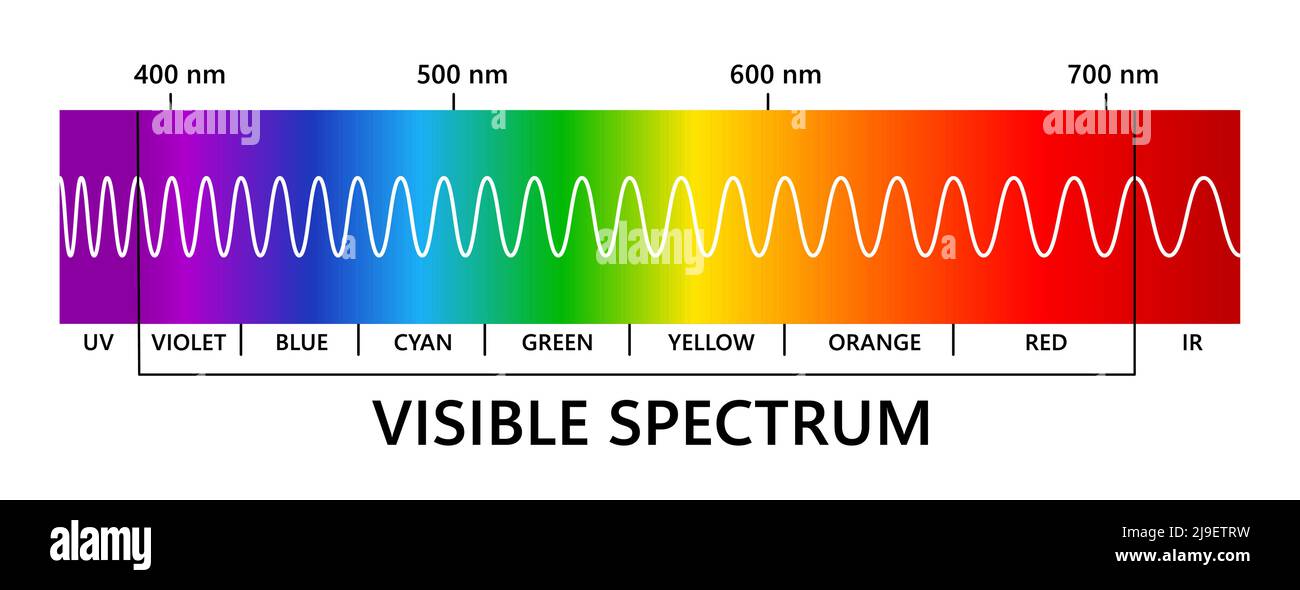
Shining white light through a prism causes the wavelengths to bend at slightly different angles due to optical refraction. Black on the other hand is what our eyes. The visible spectrum shows the wavelengths of each of the component colors.
The resulting light is split across the visible color. The wavelengths that we can see. How do we see color wavelength.
Color theory combines much of the information we know about color and turns it into a design tool. For example the color yellow results from green and red cones. This is because different colors of lights have different wavelengths.
White is what we see when all wavelengths of light are reflected off an object while pink is a mix of the red and violet wavelengths. In our forest objects are being hit by the white light of the sun which. In short the brain can easily be tricked to see.
The visible spectrum showing the wavelengths of each of the component colours. Visible light is essentially just a name for a very specific spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. This overlap along with the brain processing the simultaneous signals sent to it actually allows us to see millions of colors.
Light is made up of wavelengths of light and each wavelength is a particular colour. The objects we see around us on the other hand do not shine with their own light and reflect only particular electromagnetic wavelengths from the visible spectrum after absorbing all the. This mix of colors and white light is what lets us see colored objects.
Visible Light Spectrum Infared And Ultraviolet Light Wavelength Electromagnetic Visible Color Spectrum For Human Eye Gradient Diagram Educational Stock Vector Image Art Alamy

Colour The Visible Spectrum Britannica
Color And Absorption Spectroscopy
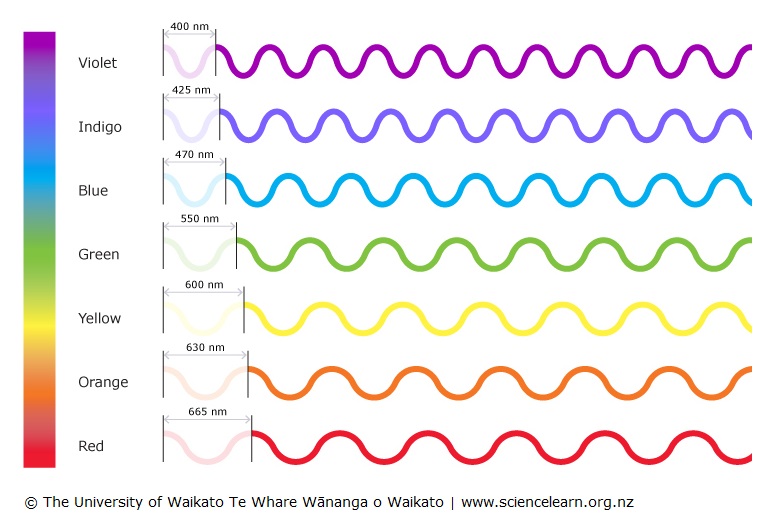
Colours Of Light Science Learning Hub

Blue Light And Health Plus How To Make Your Own Blue Blocking Glasses Light Science Color Wavelengths Physics And Mathematics

Wavelength And Color Maple Help

Jacobs Physics Mail Time Is Color Determined By Wavelength Or Frequency

List The Order Of Colors In The Color Spectrum Homework Study Com

Why Nasa Scientists Observe The Sun In Different Wavelengths Nasa

Wavelength To Colour Relationship Academo Org Free Interactive Education
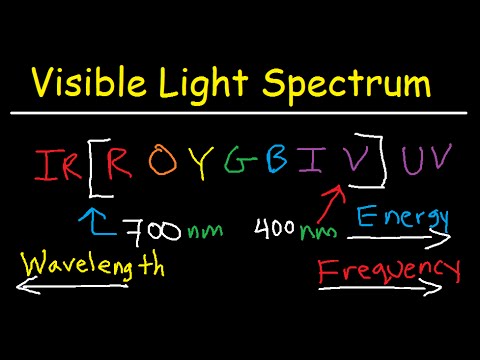
Visible Light Spectrum Explained Wavelength Range Color Chart Diagram Chemistry Youtube
/the-visible-light-spectrum-2699036_FINAL2-c0b0ee6f82764efdb62a1af9b9525050.png)
Visible Light Spectrum Overview And Chart

Electromagnetism Can Every Color In The Rgb Space Be Generated With A Single Wavelength Em Wave Physics Stack Exchange

How Can We Experience The Colors That Aren T In The Real Color Spectrum Example There Is No Wavelength Corresponding To Cyan Update Brown Quora